Start your free trial. Dydx Pxy Qxy n where n is any Real Number but not 0 or 1.

First Order Circuits 2 Circuit Analysis Circuit Analysis First Order
The relationship between the halflife denoted T 12 and the rate constant k can easily be found.

. We find the integrating factor. This step-by-step program has the ability to solve many types of first-order equations such as separable linear Bernoulli exact and homogeneous. Solving a first order differential equation.
Y re rx y r 2 e rx. The solution of this separable firstorder equation is where x o denotes the amount of substance present at time t 0. There are many tricks to solving Differential Equations if they can be solvedBut first.
Two examples are given below one for a mechanical system and one for an electrical system. 14 15 16 and 18 are of second order. 17 is of third order.
Using the boundary condition and identifying the terms corresponding to the general solution the. If you know what the derivative of a function is how can you find the function itself. We solve it when we discover the function y or set of functions y.
Your first 5 questions are on us. Next substitute the values of y y and y in y - 9y 20y 0. Origin of the First Order Differential Equation.
Well need to apply the formula for solving a first-order DE see Linear DEs of Order 1 which for these variables will be. Linearity means that all instances of the unknown and its derivatives enter the equation linearly. Related Symbolab blog posts.
In addition it solves higher-order equations with methods like undetermined coefficients variation of parameters the method of Laplace transforms and many more. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives that is an equation of the form where and are arbitrary differentiable functions that do not need to be linear and are the successive derivatives of the unknown function y of the. Free second order differential equations calculator - solve ordinary second order differential equations step-by-step.
IeintPdtintQeintPdtdt We have P50 and Q5. Ux emx 82 in which m is a constant to be determined by the following procedure. Equation b is a first order ordinary differ ential equation involving the function T ωt and the method of obtaining the general solution of th is equation is available in Chapter 7.
Consider the differential equation given by. Is there a method for solving ordinary differential equations when you are given an initial condition that will work when other methods fail. An equation with the function y and its derivative dy dx.
One such class is partial differential equations PDEs. 933 Fourier transform method for solution of partial differential equations- Contd. The graph of this equation Figure 4 is known as the exponential decay curve.
The Wolfram Language s differential equation solving functions can be applied to many different classes of differential equations automatically selecting the appropriate algorithms without the need for preprocessing by the user. How to solve this special first order differential equation. Why Are Differential Equations Useful.
A partial differential equation or briefly a PDE is a mathematical equation that involves two or more independent variables an unknown function dependent on those variables and partial derivatives of the unknown function with respect to the independent variablesThe order of a partial differential equation is the order of the highest derivative involved. When n 0 the equation can be solved as a First Order Linear Differential Equation. The order of a partial di erential equation is the order of the highest derivative entering the equation.
He solves these examples and others. A Bernoulli equation has this form. Advanced Math Solutions Ordinary Differential Equations Calculator Linear ODE.
Application Areas Power Systems Engineering Electrical Engineering Calculations Mechanical Engineering Calculations System Simulation Analysis Digital TwinsVirtual Commissioning Battery Modeling and Design Heat Transfer Modeling Dynamic Analysis of Mechanisms Calculation Management Model-Based Systems. In fact there are several ways of solving differential equations but sometimes even these methods which you will learn in future lessons will sometimes fail or be too difficult to solve by hand. Since the given differential equation is homogeneous we will assume the solution of the form y e rx Find the first and second derivative of y e rx.
An ordinary differential equation ODE is an equation that involves some ordinary derivatives as opposed to partial derivatives of a functionOften our goal is to solve an ODE ie determine what function or functions satisfy the equation. In all these cases y is an unknown function of x or of x 1 and x 2 and f is a given function. What are ordinary differential equations ODEs.
In examples above 12 13 are of rst order. When n 1 the equation can be solved using Separation of Variables. 82 Typical form of second-order homogeneous differential equations p243 0 2 2 bu x dx du x a d u x 81 where a and b are constants The solution of Equation 81 ux may be obtained by ASSUMING.
This is a first order linear differential equation. IFeint50dte50t So after substituting into the formula we have. Differential equations first came into existence with the invention of calculus by Newton and LeibnizIn Chapter 2 of his 1671 work Methodus fluxionum et Serierum Infinitarum Isaac Newton listed three kinds of differential equations.
A Differential Equation is a n equation with a function and one or more of its derivatives. Solve the second order differential equation y - 9y 20y 0 Solution. If the assumed solution ux in Equation 82 is a valid solution it must SATISFY.
Capacitor Discharge An application of homogeneous differential equations A first order homogeneous differential equation has a solution of the form. The differential equation with input ft and output yt can represent many different systems. For the process of discharging a capacitor C which is initially charged to the voltage of a battery V b the equation is.

Applications Of First Order Differential Equations Mixing Concentrations Differential Equations Equations Concentration

Applications Of First Order Differential Equations Exponential Decay Pa Differential Equations Exponential Equations

Shortcut Reduction Of Order Linear Second Order Homogeneous Differenti Differential Equations Equations Reduction

Solve A First Order Homogeneous Differential Equation 3 Differential Differential Equations Equations Solving

Applications Of First Order Differential Equations Newton S Law Of Coo Differential Equations Equations Newtons Laws

Applications Of First Order Differential Equations Exponential Decay P Differential Equations Exponential Equations

Applications Of First Order Differential Equations Mixing Concentratio Differential Equations Equations Physics And Mathematics

How To Solve The Linear Third Order Differential Equation Y 6y Differential Equations Math Videos Solving

Solve A First Order Homogeneous Differential Equation 1 Differential Free Math Help Mathematical Expression Math Methods

First Order Partial Differential Equations Vol 2 Partial Differential Equation Differential Equations Introduction To Quantum Mechanics

Intro To Initial Value Problems 2 Differential Equations Differential Equations Equations Intro

First Order Linear Differential Equation Integrating Factor Idea Stra Differential Equations Linear Equations Linear Differential Equation

Differential Equation 1st Order Linear Applications I T Of The R Differential Equations Equations Equation

First Order Linear Differential Equation Integrating Factor Idea Stra Differential Equations Linear Equations Linear Differential Equation

Exact First Order Differential Equations 2 Differential Equations Differential Equations Equations Physics And Mathematics
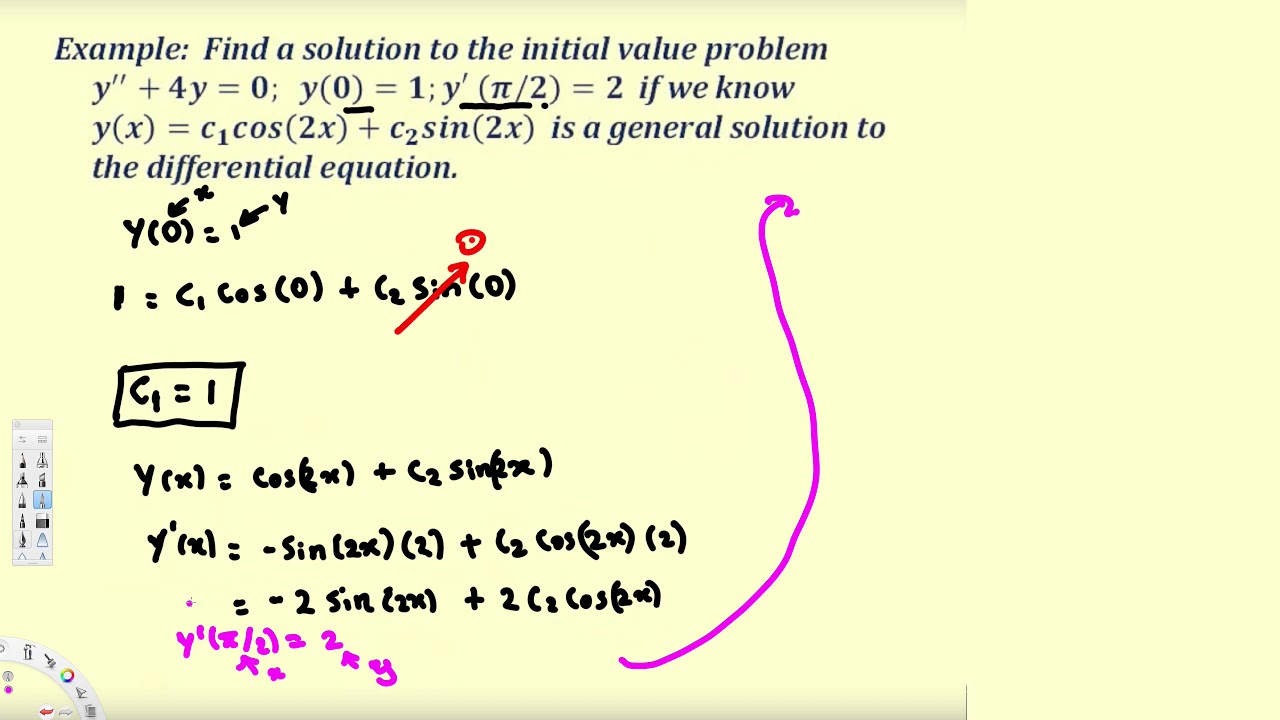
Intro Boundary Value Problems 2 Differential Equations Differential Equations Equations Intro

Newton S Law Of Cooling Calculus Example Problems Differential Equations Newtons Laws Differential Equations Equations

Ex 1 Solve A Linear Second Order Homogeneous Differential Equation Ini Differential Equations Solving Equations

Application On First Ode Newton S Law Of Cooling Newtons Laws Differential Equations Equations

